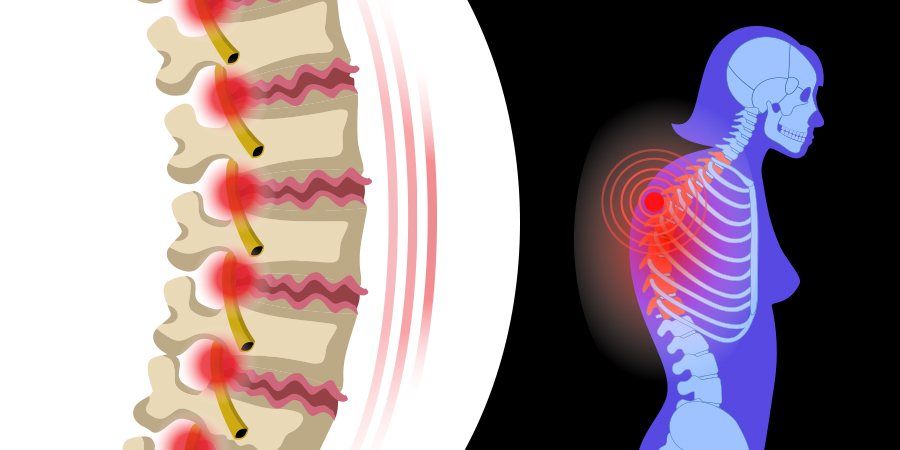
- What is Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis, referred to as degenerative joint disease, occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones deteriorates or thins out. This degeneration leads to inflammation and pain. Additionally, it can result in the formation of osteophytes, commonly known as bone spurs.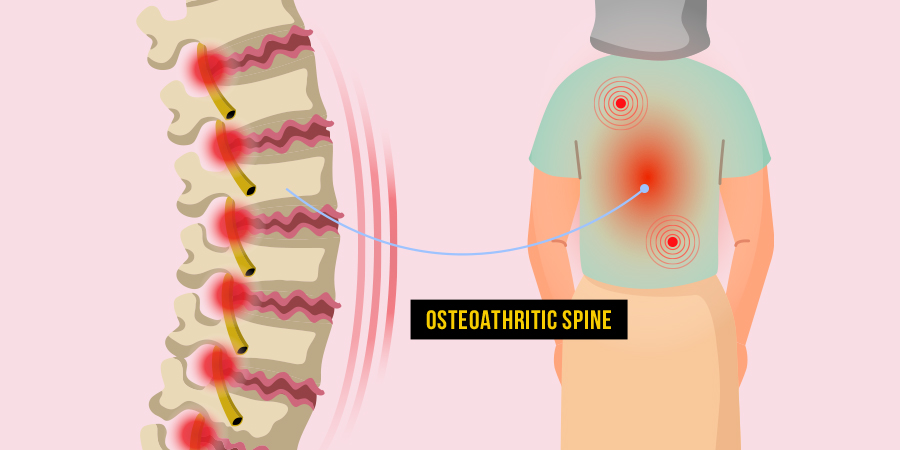
- What is Osteoarthritis of the Spine
Osteoarthritis of the spine involves the deterioration of cartilage in the joints and discs located in the cervical and lumbar regions. In some cases, this condition leads to the formation of spurs that exert pressure on the nerves exiting the spinal column, resulting in symptoms like weakness and pain in the arms or legs. - Cartilage Deterioration
As osteoarthritis progresses, the cartilage in the spine wears down, resulting in bone-on-bone friction, swelling, and tenderness. This process can lead to the formation of bone spurs and joint malformation. - Impacted Regions: Cervical and Lumbar
Both the cervical (neck) and lumbar (lower back) regions are susceptible to spinal osteoarthritis, causing varying degrees of pain, stiffness, and reduced flexibility. In advanced cases, nerve compression and radiating pain may occur.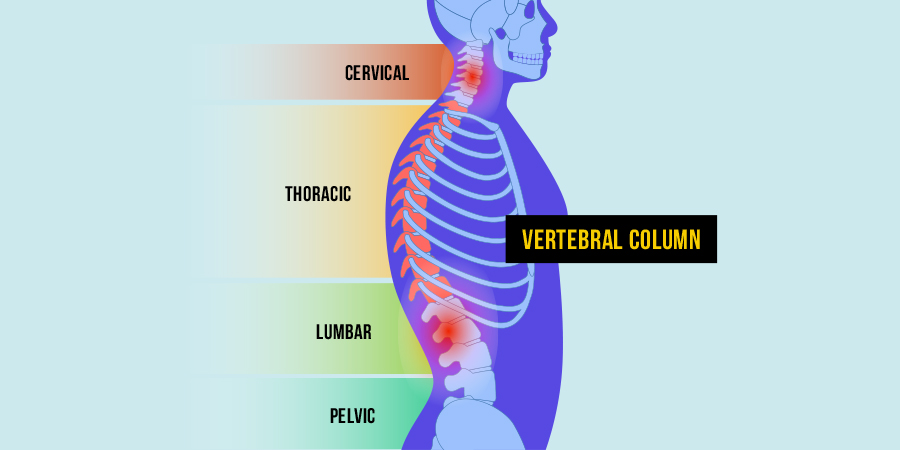
- Signs and Symptoms
Common symptoms of spinal osteoarthritis include localized pain, stiffness, reduced range of motion, and muscle weakness. Nerve compression symptoms like radiating pain or numbness may also present with disease progression. - Age as a Risk Factor
Advancing age is a significant risk factor for developing spinal osteoarthritis due to the cumulative effects of wear and tear on the spine over time. Older individuals are more prone to degenerative changes that contribute to osteoarthritis development. - Genetic Predisposition
Genetic factors can play a role in predisposing individuals to spinal osteoarthritis, influencing the disease’s severity and progression. Certain genetic markers may increase susceptibility to cartilage degeneration and joint inflammation.
- Impact of Weight on Spinal Joints
Excess weight and obesity can impose additional stress on spinal joints, exacerbating degeneration and accelerating the progression of osteoarthritis. Weight management and maintaining a healthy body mass index are essential in managing spinal osteoarthritis. - Trauma and Accelerated Degeneration
Spinal injuries or trauma can lead to the hastened degeneration of vertebral joints, increasing the likelihood of developing osteoarthritis. Traumatic events can initiate or exacerbate the structural changes that contribute to joint degeneration over time. - Repetitive Stress and Joint Health
Repetitive activities or occupational stress can contribute to the breakdown of spinal joints, accelerating the degenerative process. Continuous wear-and-tear from repetitive movements can exacerbate cartilage damage and joint inflammation in the spine. - Diagnosis of Spinal Osteoarthritis
Diagnosing spinal osteoarthritis involves a combination of physical examinations, imaging tests like X-rays and MRIs, and symptom evaluation. Identifying specific degenerative changes in the spine helps in formulating appropriate treatment strategies tailored to each patient.
- Treatment Modalities for Spinal Osteoarthritis
Treatment options for spinal osteoarthritis encompass conservative measures like pain management, physical therapy, exercise, lifestyle modifications, and, in severe cases, surgical interventions. A multidisciplinary approach is often employed to address pain, improve function, and slow disease progression. - Medications for Pain Management
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), analgesics, and corticosteroid injections are commonly used to manage pain and inflammation in spinal osteoarthritis. These medications can help alleviate discomfort, reduce swelling, and improve overall quality of life for individuals with the condition.
- Role of Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing spinal osteoarthritis by improving strength, flexibility, and mobility. Therapeutic exercises and techniques can help alleviate pain, enhance joint function, and prevent further degeneration of the spine. - Exercise for Joint Health
Engaging in regular physical activity promotes joint health by maintaining flexibility, strength, and range of motion in the spine. Low-impact exercises like swimming, walking, and yoga can help strengthen supporting muscles and reduce pain associated with osteoarthritis.
- Lifestyle Modifications for Spinal Osteoarthritis
Adopting lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and avoiding activities that strain the spine can slow the progression of osteoarthritis. Adjusting daily habits and ergonomics can minimize stress on spinal joints and improve overall spinal health. - Surgical Interventions for Severe Cases
In advanced or refractory cases of spinal osteoarthritis, surgical interventions like spinal fusion or decompression may be considered. These procedures aim to alleviate nerve compression, stabilize the spine, and improve the patient’s quality of life. - Chronic Nature of the Condition
Spinal osteoarthritis is a chronic condition that requires long-term management to control symptoms and prevent progression. Patients with osteoarthritis of the spine may need ongoing treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and monitoring to maintain spinal health. - Research Advancements in Spinal Osteoarthritis
Ongoing research aims to explore innovative treatments, diagnostic tools, and interventions for spinal osteoarthritis. Advances in regenerative medicine, biologics, and personalized therapies offer hope for improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life for patients.
- Alternative Therapies for Managing Symptoms
Complementary treatments like acupuncture, chiropractic care, and massage therapy may provide symptomatic relief for individuals with spinal osteoarthritis. These alternative therapies can help alleviate pain, reduce stress, and improve overall well-being in combination with conventional treatments. - Connection to Spinal Stenosis
Osteoarthritis of the spine is closely linked to the development of spinal stenosis, a condition characterized by narrowing of the spinal canal. The degenerative changes associated with osteoarthritis can contribute to spinal stenosis symptoms, including spinal cord compression and radiating pain.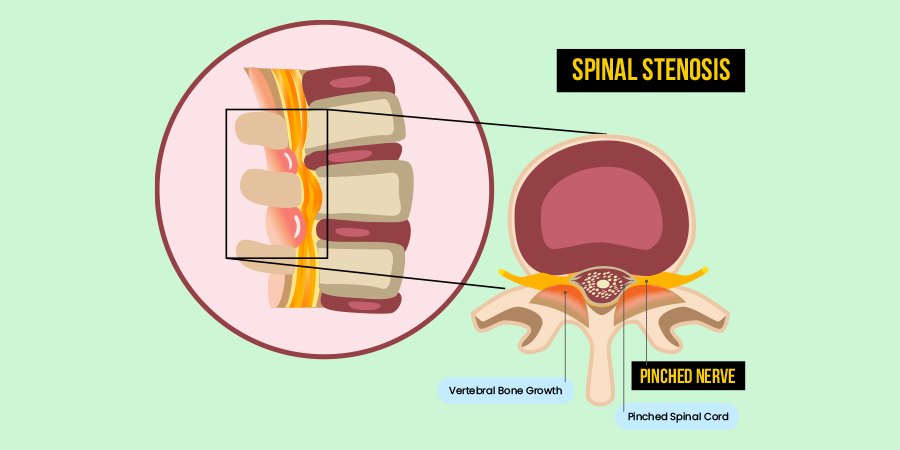
- Importance of Proper Ergonomics
Maintaining proper posture and ergonomics at work and home is essential for managing spinal osteoarthritis. Correct body mechanics, ergonomic adjustments, and supportive devices can reduce spinal strain, alleviate discomfort, and prevent exacerbation of symptoms. - Nutritional Support for Joint Health
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and antioxidants can support joint health in individuals with osteoarthritis. Consuming foods that reduce inflammation and promote cartilage maintenance can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
- Yoga and Pilates for Spinal Health
Yoga and Pilates exercises focus on improving flexibility, strength, and posture, making them beneficial for individuals with spinal osteoarthritis. These mind-body practices can enhance spinal mobility, alleviate pain, and promote relaxation in individuals managing osteoarthritis of the spine.
- Use of Bracing and Orthotics
Braces, orthotic devices, and supportive equipment can help stabilize the spine, reduce pain, and improve spinal alignment in individuals with osteoarthritis. These assistive devices support the affected joints, alleviate pressure, and enhance functional abilities for patients with spinal osteoarthritis. - Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat or cold packs to the affected areas can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with spinal osteoarthritis. Heat therapy increases blood flow, relaxes muscles, and alleviates stiffness, while cold therapy numbs the area, reduces swelling, and provides temporary pain relief. - Psychological Support for Coping
Emotional support, counseling, and psychological interventions play a vital role in helping individuals cope with chronic pain and the challenges of spinal osteoarthritis. Managing the psychological impact of the condition can improve mental well-being, enhance quality of life, and promote resilience in patients. - Postural Exercises and Techniques
Postural exercises, ergonomic adjustments, and spine-strengthening techniques can promote proper spinal alignment and reduce strain on affected joints. Incorporating postural awareness into daily activities can help alleviate pain, improve posture, and prevent worsening of osteoarthritis symptoms.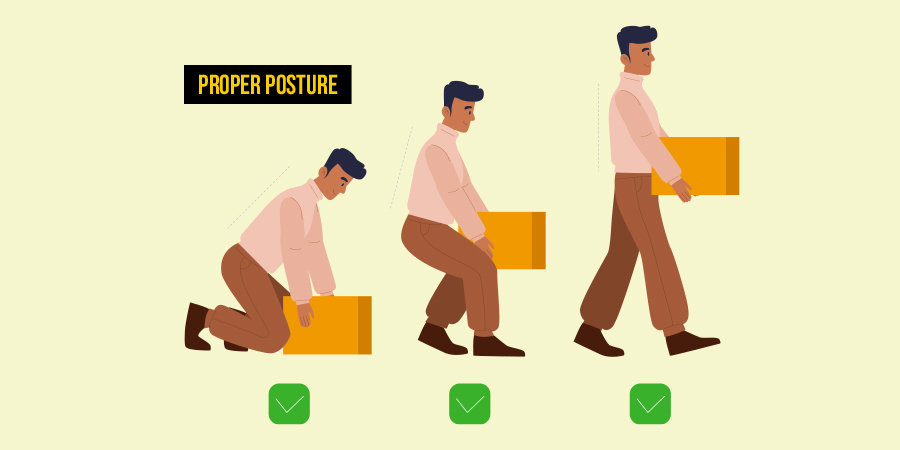
- Patient Education on Self-Care
Empowering patients with knowledge about their condition, treatment options, and self-care strategies is essential for effective management of spinal osteoarthritis. Educating individuals on lifestyle modifications, exercise routines, and symptom management enhances their ability to actively participate in their care and improve outcomes. - Complementary Therapies for Relief
Incorporating complementary therapies like aromatherapy, mindfulness practices, and relaxation techniques can complement conventional treatments for spinal osteoarthritis. These holistic approaches can reduce stress, promote relaxation, and provide additional support in pain management for individuals with the condition. - Benefits of Hydrotherapy
Hydrotherapy, involving water-based exercises in a therapeutic pool, can improve mobility, reduce pain, and enhance joint flexibility for individuals with osteoarthritis. The buoyancy of water supports the body, decreases weight-bearing stress on joints, and facilitates gentle movement without excessive strain on the spine.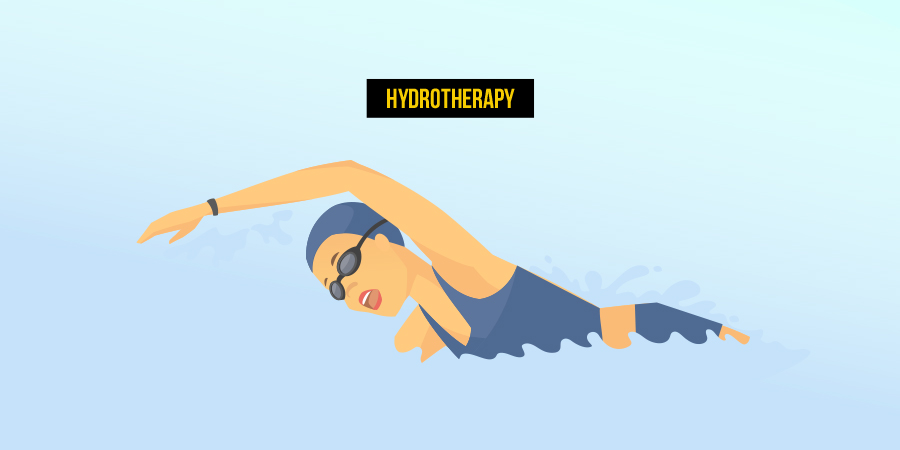
- Active Participation in Treatment
Active engagement in treatment plans, adherence to therapy regimens, and lifestyle modifications are crucial for managing spinal osteoarthritis effectively. Taking an active role in self-care, exercise programs, and treatment decisions can improve outcomes, reduce symptoms, and slow disease progression. - Social Support and Connection
Building a supportive network, connecting with others facing similar challenges, and seeking encouragement can enhance emotional well-being in individuals with spinal osteoarthritis. Social support systems provide reassurance, understanding, and motivation for coping with the impact of the condition on daily life.
- Use of Assistive Devices
Utilizing assistive devices like canes, walkers, or adaptive tools can assist individuals with spinal osteoarthritis in performing daily activities with ease. These aids enhance mobility, reduce joint strain, and promote independence in patients experiencing limitations due to the condition.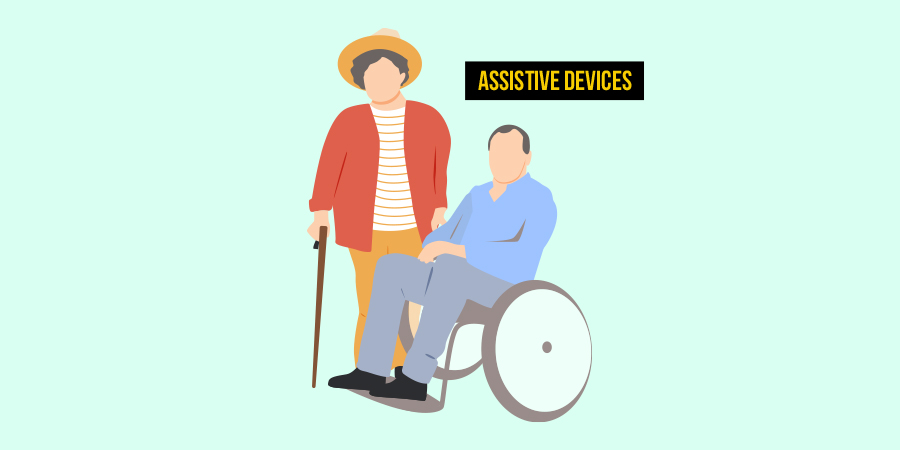
- Importance of Sleep Hygiene
Maintaining good sleep habits, creating a conducive sleep environment, and managing pain to improve sleep quality are essential for individuals with spinal osteoarthritis. Adequate rest, relaxation techniques, and pain management strategies can enhance sleep hygiene and promote overall well-being in patients. - Strategies for Pacing Activities
Balancing activities, pacing tasks, and taking frequent breaks can prevent overexertion and manage fatigue in individuals with spinal osteoarthritis. Implementing strategies that break tasks into manageable segments can conserve energy, reduce strain on joints, and prevent symptom exacerbation. - Stress Management Techniques
Incorporating stress management techniques, mindfulness practices, and relaxation exercises can help individuals cope with the emotional toll of spinal osteoarthritis. Managing stress levels, practicing relaxation techniques, and seeking emotional support can improve mental health and overall quality of life. - Monitoring and Follow-up Care
Regular monitoring, follow-up appointments, and assessments are essential for tracking disease progression and adjusting treatment plans for spinal osteoarthritis. Continual evaluation, imaging studies, and consultation with healthcare providers ensure proper management and timely intervention for optimal outcomes.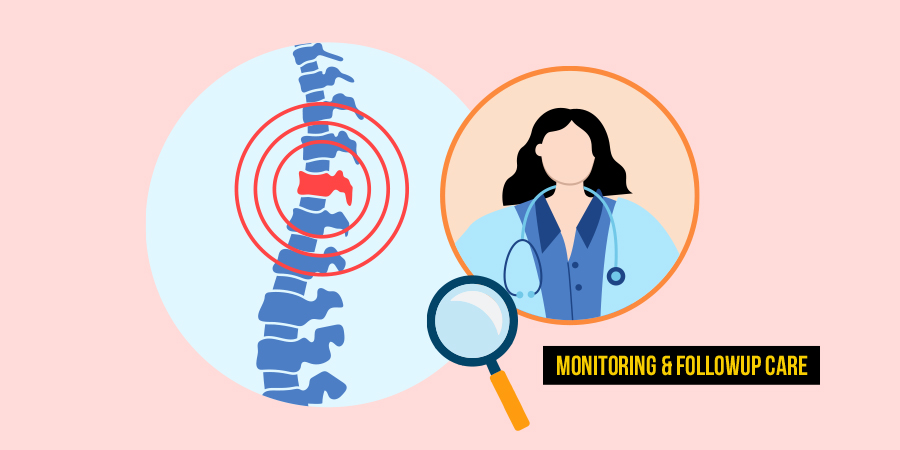
- Staying Informed and Empowered
Staying informed about the latest research, treatment options, and self-care strategies empowers individuals to make informed decisions about managing spinal osteoarthritis. Education, engagement, and advocacy play a key role in promoting self-empowerment, enhancing treatment adherence, and improving overall quality of life. - Continual Self-Empowerment
Continuous education, active participation in care, and self-advocacy are essential for individuals navigating the challenges of spinal osteoarthritis. Empowering individuals with knowledge, resources, and support fosters self-efficacy, resilience, and a proactive approach to managing the condition effectively.
References
- What is Osteoarthritis
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/osteoarthritis/symptoms-causes/syc-20351925 - What is Osteoarthritis of the Spine
https://www.webmd.com/osteoarthritis/spinal-osteoarthritis-degenerative-arthritis-of-the-spine - Cartilage Deterioration
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/osteoarthritis/symptoms-causes/syc-20351925 - Impacted Regions: Cervical and Lumbar
https://www.hss.edu/conditions_spondylosis-overview.asp - Signs and Symptoms
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/spinal-arthritis - Age as a Risk Factor
https://www.arthritis-health.com/types/osteoarthritis/spinal-osteoarthritis-risk-factors - Genetic Predisposition
https://www.healthline.com/health/is-osteoarthritis-genetic#genetic - Impact of Weight on Spinal Joints
https://www.arthritis.org/health-wellness/about-arthritis/related-
conditions/other-diseases/how-fat-affects-osteoarthritis - Trauma and Accelerated Degeneration
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1063458419311148 - Repetitive Stress and Joint Health
https://www.tgh.org/institutes-and-services/conditions/osteoarthritis - Diagnosis of Spinal Osteoarthritis
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/spinal-arthritis - Treatment Modalities for Spinal Osteoarthritis
https://www.physio-pedia.com/Spinal_Osteoarthritis#:~:text=pain.%5B3%5D-,Physiotherapy,-One%20of%20the - Medications for Pain Management
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547742/ - Role of Physical Therapy
https://www.arthritis.org/health-wellness/treatment/complementary-therapies/physical-therapies/osteoarthritis-physical-therapy - Exercise for Joint Health
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/arthritis/in-depth/arthritis/art-20047971 - Lifestyle Modifications for Spinal Osteoarthritis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2603303/ - Surgical Interventions for Severe Cases
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9319328/ - Chronic Nature of the Condition
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352320420300651 - Research Advancements in Spinal Osteoarthritis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9072900/ - Benefits of Tailored Physical Activity
https://www.oarsijournal.com/article/S1063-4584(20)30325-3/fulltext - Connection to Spinal Stenosis
https://www.arthritis-health.com/types/osteoarthritis/how-osteoarthritis-can-lead-spinal-stenosis - Importance of Proper Ergonomics
https://www.webmd.com/arthritis/features/ergonomics-at-work - Nutritional Support for Joint Health
https://www.hackensackmeridianhealth.org/en/healthu/2024/07/10/nutrition-for-joint-health - Yoga and Pilates for Spinal Health
https://www.hrosm.com/the-benefits-of-pilates-and-yoga-for-spine-health/#:~:text=Pilates%20and%20yoga%20have%20been,muscles%2C%20providing%20relief%20from%20pain - Use of Bracing and Orthotics
https://www.healthline.com/health/types-of-osteoarthritis-braces#:~:text=Braces%20for%20osteoarthritis%20may%20help,and%20may%20restrict%20your%20mobility - Heat and Cold Therapy
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/heat-or-ice-for-arthritis#:~:text=Both%20heat%20and%20cold%20therapy,the%20uncomfortable%20symptoms%20of%20arthritis - Psychological Support for Coping
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK73528/ - Postural Exercises and Techniques
https://www.physio-pedia.com/Osteoarthritis_and_Exercise - Patient Education on Self-Care
https://www.webmd.com/osteoarthritis/osteoarthritis-10-tips - Complementary Therapies for Relief
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3857560/ - Benefits of Hydrotherapy
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8955208/ - Active Participation in Treatment
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8955940/ - Social Support and Connection
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5964569/ - Use of Assistive Devices
https://www.webmd.com/arthritis/features/living-easier-arthritis-devices - Importance of Sleep Hygiene
https://www.arthritisnsw.org.au/sleep-hygiene-arthritis/ - Strategies for Pacing Activities
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3162944/ - Stress Management Techniques
https://www.webmd.com/arthritis/features/reduce-stress-ease-pain - Monitoring and Follow-up Care
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/330487-treatment#d12 - Staying Informed and Empowered
https://arthritis.ca/about-arthritis/arthritis-types-(a-z)/types/osteoarthritis/osteoarthritis-self-management - Continual Self-Empowerment
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2665913124000311
If you need treatment options in Tulsa, Oklahoma for Osteoarthritis, request an appointment with Dr. James Webb.
One of the leading experts in addressing and preventing spinal compression fractures.
Keep yourself updated, take proactive steps, and make your spinal health a top priority for a brighter future ahead.

